Slaking
 Slaking is the breakdown of large, air-dry soil aggregates (>2-5 mm) into smaller sized microaggregates (<0.25 mm) when they are suddenly immersed in water. Slaking occurs when aggregates are not strong enough to withstand internal stresses caused by rapid water uptake. Internal stresses result from differential swelling of clay particles, trapped and escaping air in soil pores, rapid release of heat during wetting, and the mechanical action of moving water.
Slaking is the breakdown of large, air-dry soil aggregates (>2-5 mm) into smaller sized microaggregates (<0.25 mm) when they are suddenly immersed in water. Slaking occurs when aggregates are not strong enough to withstand internal stresses caused by rapid water uptake. Internal stresses result from differential swelling of clay particles, trapped and escaping air in soil pores, rapid release of heat during wetting, and the mechanical action of moving water. In contrast to slaking, tests for aggregate stability measure how well soil withstands external destructive forces, such as the splashing impact of raindrops. Both poor aggregate stability and slaking result in detached soil particles that settle into pores, and cause surface sealing, reduced infiltration and plant available water, and increased runoff and erosion.
Relationship to Soil Function
Slaking indicates the stability of soil aggregates, resistance to erosion and suggests how well soil can maintain its structure to provide water and air for plants and soil biota when it is rapidly wetted. Limited slaking suggests that organic matter is present in soil to help bind soil particles and microaggregates into larger, stable aggregates.
Problems with Poor Function
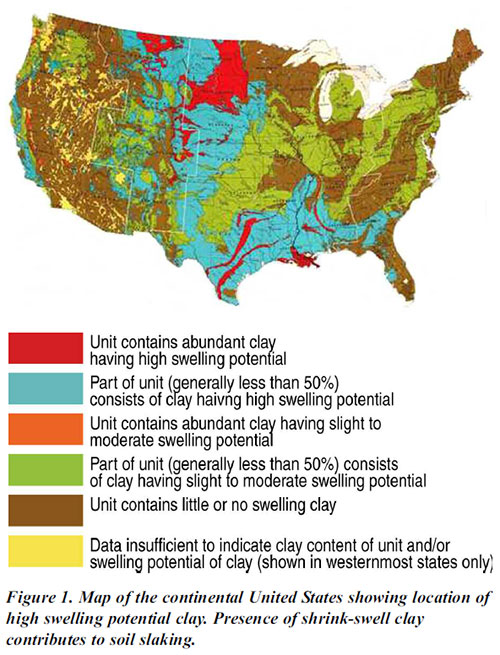 Slaked soil particles block soil pores, form a soil crust, reduce infiltration and water movement through soil, and increase runoff and erosion. Small aggregates produced by slaking settle together resulting in smaller pore spaces than where present with larger aggregates. Pore volume may be reduced and the ability of plants to use water stored in pore spaces may be altered.
Slaked soil particles block soil pores, form a soil crust, reduce infiltration and water movement through soil, and increase runoff and erosion. Small aggregates produced by slaking settle together resulting in smaller pore spaces than where present with larger aggregates. Pore volume may be reduced and the ability of plants to use water stored in pore spaces may be altered.
Conservation practices that lead to slaking include:
- Conventional tillage methods that disturb soil and accelerate organic matter decomposition,
- Burning, harvesting or otherwise removing crop residues, and
- Using pesticides harmful to soil organisms that cycle organic matter and promote aggregation.
Avoiding Slaking
Conservation tillage systems, such as no-till, reduce slaking by reducing soil disturbing activities that break aggregates apart and accelerate decomposition of organic matter. No-till and residue management lead to increased soil organic matter and improved aggregate stability and soil structure, particularly when cover crops or sod-based rotations provide an additional source of residue.
Conservation practices that minimize slaking include:
- Conservation Crop Rotation
- Cover Crops
- Prescribed Grazing
- Residue and Tillage management
This Page Was Created Utilizing Text And Images From These Sources:
Slaking, Soil Quality Indicators Fact Sheet- USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service

West River Soil Health School Registration Open!
In 2024, the South Dakota Soil Health Coalition will host an additional Soil Health School in west of the Missouri River! The 2024 West River Soil Health School with be held June 26-27 near Caputa, SD! This school will focus on issues specific to the land, climate, and ag production systems of wester South Dakota. Class size is limited, so early registration is strongly encouraged!
News & Events
Farmer reaps higher yields by interseeding soybeans
By Stan Wise Alex Frasier has spent a lot of time studying what it takes to grow a successful crop. After studying ag production and precision technology at Lake Area Technical College, he has worked in ag retail and currently works as an agronomist in Aberdeen, SD....
Farm and ranch innovators to share new ideas at Soil Health Conference
By Stan Wise PIERRE, SD — Before Cooper Hibbard came home to manage his family’s ranch, he studied ag business, rangeland resources and Spanish at California Polytechnic State University and then worked on ranches all over the world. That education and experience...
Wintertime is decision time
By Stan Wise PIERRE, SD – It’s often said that the best time to start improving your land was 20 years ago, but the second-best time is right now. That statement might be harder for ranchers to swallow with winter on their doorstep, nothing growing in their pastures,...


