Particulate Organic Matter
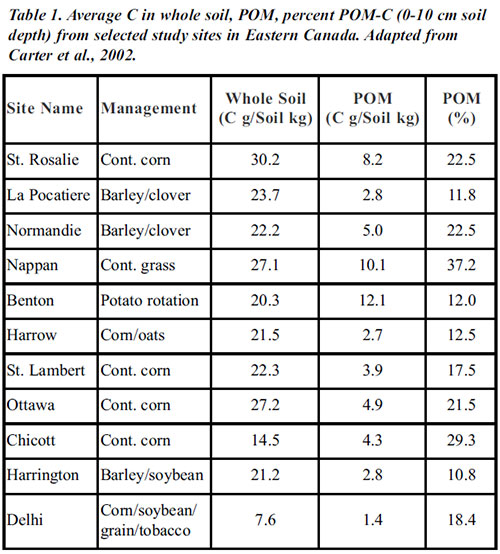
 Particulate organic matter (POM) fraction referred to in this document comprises all soil organic matter (SOM) particles less than 2 mm and greater than 0.053 mm in size (Cambardella and Elliot, 1992). POM is biologically and chemically active and is part of the labile (easily decomposable) pool of soil organic matter (SOM). Figure 1 shows tiny debris of POM (0.25 mm < POM size < 0.5 mm) at different stages of decomposition isolated from soil under no-till management. Studies have shown that POM accounts for few to large amounts of soil C (20% and more) in some soils of Eastern Canada and the USA depending upon agroecosystems and management practices (Table1).
Particulate organic matter (POM) fraction referred to in this document comprises all soil organic matter (SOM) particles less than 2 mm and greater than 0.053 mm in size (Cambardella and Elliot, 1992). POM is biologically and chemically active and is part of the labile (easily decomposable) pool of soil organic matter (SOM). Figure 1 shows tiny debris of POM (0.25 mm < POM size < 0.5 mm) at different stages of decomposition isolated from soil under no-till management. Studies have shown that POM accounts for few to large amounts of soil C (20% and more) in some soils of Eastern Canada and the USA depending upon agroecosystems and management practices (Table1). Relationship to Soil Function
As perhaps the most easily decomposable fraction of nonliving SOM after microbial biomass, POM fulfills many soil functions mediated by OM. It is a source of food/energy for microorganisms and soil animals as well as nutrients for plant growth. Particulate organic matter enhances aggregate stability, water infiltration and soil aeration; it increases cation exchange capacity and buffering pH. It also binds environmental pollutants such as heavy metals and pesticides. Particulate organic matter may play an important role in the suppression of soil borne diseases (e.g. damping off of cucumber) by compost. This may be explained by the fact that POM is an important source of food/energy in the compost for microorganisms responsible of disease suppression.
POM and Poor Soil Function
 In poorly managed soils, the transport by erosion of sediments rich in POM into rivers and other water bodies can result in alteration of water quality and aquatic life. Build up and mineralization of those organic materials lead to the eutrophication of lakes and rivers. Incomplete mineralization of POM C in very poorly drained soils can lead to the formation of methane, which escapes into the atmosphere and contributes to ozone depletion.
In poorly managed soils, the transport by erosion of sediments rich in POM into rivers and other water bodies can result in alteration of water quality and aquatic life. Build up and mineralization of those organic materials lead to the eutrophication of lakes and rivers. Incomplete mineralization of POM C in very poorly drained soils can lead to the formation of methane, which escapes into the atmosphere and contributes to ozone depletion.
Improving POM Levels
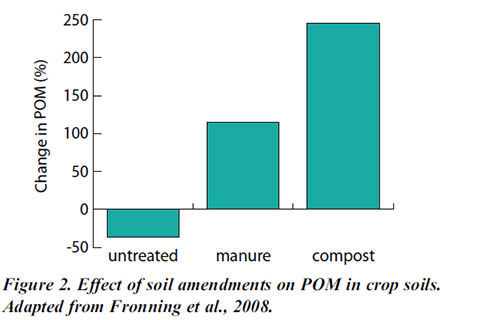 Management that affects SOM accumulation also affects POM content in soil (figs 2 and 3). More POM in the soil means that carbon and other nutrients are being stored in the intermediately available pool and are not subjected to losses (e.g., leaching) yet are available when needed.
Management that affects SOM accumulation also affects POM content in soil (figs 2 and 3). More POM in the soil means that carbon and other nutrients are being stored in the intermediately available pool and are not subjected to losses (e.g., leaching) yet are available when needed.
The following practices enhance POM levels:
- Tillage management (no-till, strip till, and ridge till)
- Crop rotation, cover crops, and cropping frequency (reduction in fallow frequency)
- Application of manure/compost and organic byproducts
- Pasture and hay land management (e.g., rotational grazing and haying)
This Page Was Created Utilizing Text And Images From These Sources:

West River Soil Health School Registration Open!
In 2024, the South Dakota Soil Health Coalition will host an additional Soil Health School in west of the Missouri River! The 2024 West River Soil Health School with be held June 26-27 near Caputa, SD! This school will focus on issues specific to the land, climate, and ag production systems of wester South Dakota. Class size is limited, so early registration is strongly encouraged!
News & Events
Farmer reaps higher yields by interseeding soybeans
By Stan Wise Alex Frasier has spent a lot of time studying what it takes to grow a successful crop. After studying ag production and precision technology at Lake Area Technical College, he has worked in ag retail and currently works as an agronomist in Aberdeen, SD....
Farm and ranch innovators to share new ideas at Soil Health Conference
By Stan Wise PIERRE, SD — Before Cooper Hibbard came home to manage his family’s ranch, he studied ag business, rangeland resources and Spanish at California Polytechnic State University and then worked on ranches all over the world. That education and experience...
Wintertime is decision time
By Stan Wise PIERRE, SD – It’s often said that the best time to start improving your land was 20 years ago, but the second-best time is right now. That statement might be harder for ranchers to swallow with winter on their doorstep, nothing growing in their pastures,...


