Soil Nitrate
 Nitrate (NO3 -) is a form of inorganic nitrogen (N) naturally occurring in soils. Sources of soil NO3 – include decomposing plant residues and animal manure/compost, chemical fertilizers, exudates from living plants, rainfall, and lightning. Eventually, nitrate ions immobilized by microorganisms (nitrate taken up by microorganisms) are converted into organic forms and released back to the soil in plant-available forms when dead soil organisms are fed upon or decompose. In well drained soils, ammonium (NH4 +) and ammonia (NH3) are converted into NO3 by very specific populations of aerobic bacteria. This process is known as nitrification.
Nitrate (NO3 -) is a form of inorganic nitrogen (N) naturally occurring in soils. Sources of soil NO3 – include decomposing plant residues and animal manure/compost, chemical fertilizers, exudates from living plants, rainfall, and lightning. Eventually, nitrate ions immobilized by microorganisms (nitrate taken up by microorganisms) are converted into organic forms and released back to the soil in plant-available forms when dead soil organisms are fed upon or decompose. In well drained soils, ammonium (NH4 +) and ammonia (NH3) are converted into NO3 by very specific populations of aerobic bacteria. This process is known as nitrification.
Another biological N transformation is denitrification, which is the conversion of NO3 – into nitrous oxide (N2O), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and nitrogen gas (N2) that often occurs in anaerobic soils, such as waterlogged soils and wetlands. Even when nitrifying bacteria are very active in the outer parts of aggregates in well aerated soils, denitrification may still occur in anaerobic microsites inside the aggregates. Nitrate is very soluble in water and can be easily transported by runoff and other surface and subsurface flows to rivers and lakes or moved downward to ground water.
Relationship to Soil Function
The primary function of NO3 – is to serve as a source of nitrogen for the nutrition and growth of plants and soil microorganisms.
Problems with Poor Activity
Denitrification results in nitrogen loss from soil and produces some forms of intermediate gaseous nitrogen (e.g., N2O) that are harmful to the environment. Problems associated with high NO3 – concentration include the pollution of ground water and surface water and an increased risk of eutrophication that threatens the survival of aquatic life. Nitrification can potentially result in soil acidification by hydrogen ions (H+) released during the process.
Improving Management
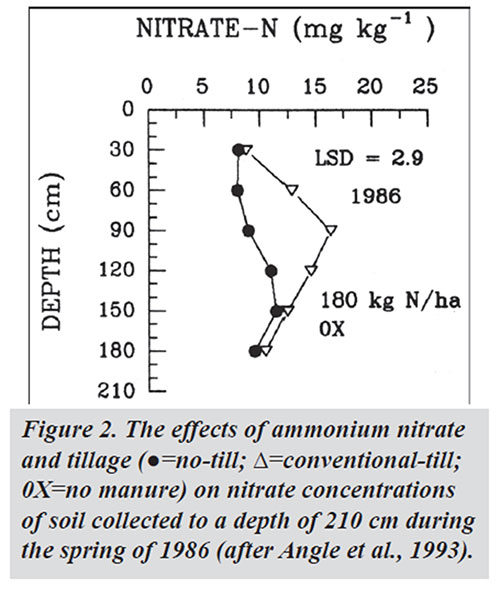
In a study conducted at the University of Maryland Research Center, soil NO3 – concentrations at any depth (except 0-30 cm) have been found to be consistently lower in no-till plots than in conventional-till plots (see Figure 2) and were related to the amount of N fertilizer applied. The explanations by the authors of the study include: (i) the lack of a winter cover crop on the conventional till plots affected the soil N content in the root zone and the subsequent rates of nitrate leaching; (ii) the no-till plots had higher rates of denitrification compared to the conventional till plots (i.e., higher populations of denitrifying organisms in no-till); (iii) crops in no-till plots used N more efficiently (removal of more N from soil); and (iv) the conventional till plots had an accumulation of nitrate from the plant residues of previous years.
The following practices add nitrate:
- Crop rotations with legumes
- Addition of organic residues, manure, and compost
- Conservation tillage and field strips or no-till with a winter cover crop
- Split applications of fertilizer that match crop growth stages
The following practices prevent nitrate loss:
- Autumn applications of ammonium-based fertilizer on frozen soils
- Application of materials that slowly release nitrogen
- Planting cover crop species that use residual NO3-
- Planning the timing and rates of irrigation according to site water content
- Keeping the soil well drained
- Additions of green manure with a high C/N ratio
This Page Was Created Utilizing Text And Images From These Sources:
Soil Nitrate, Soil Quality Indicators Fact Sheet- USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service

West River Soil Health School Registration Open!
In 2024, the South Dakota Soil Health Coalition will host an additional Soil Health School in west of the Missouri River! The 2024 West River Soil Health School with be held June 26-27 near Caputa, SD! This school will focus on issues specific to the land, climate, and ag production systems of wester South Dakota. Class size is limited, so early registration is strongly encouraged!
News & Events
Farmer reaps higher yields by interseeding soybeans
By Stan Wise Alex Frasier has spent a lot of time studying what it takes to grow a successful crop. After studying ag production and precision technology at Lake Area Technical College, he has worked in ag retail and currently works as an agronomist in Aberdeen, SD....
Farm and ranch innovators to share new ideas at Soil Health Conference
By Stan Wise PIERRE, SD — Before Cooper Hibbard came home to manage his family’s ranch, he studied ag business, rangeland resources and Spanish at California Polytechnic State University and then worked on ranches all over the world. That education and experience...
Wintertime is decision time
By Stan Wise PIERRE, SD – It’s often said that the best time to start improving your land was 20 years ago, but the second-best time is right now. That statement might be harder for ranchers to swallow with winter on their doorstep, nothing growing in their pastures,...


