Physical Properties
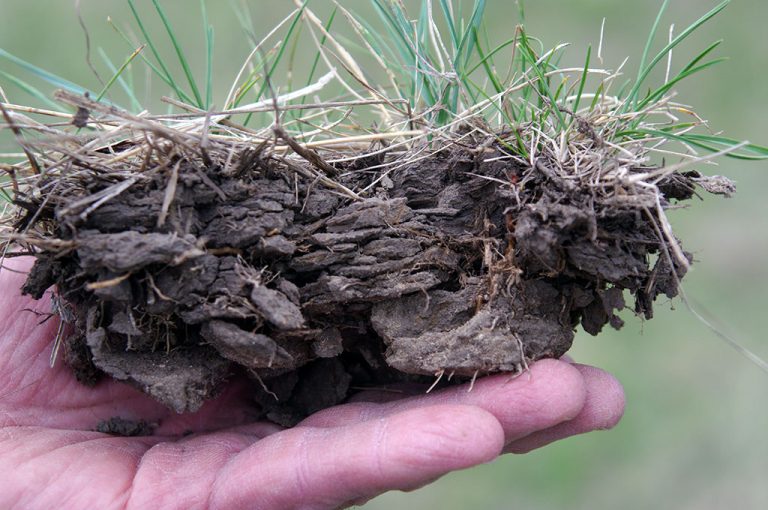

Soil Structure
Sand, silt and clay particles are the primary mineral building blocks of soil. Soil structure is the combination or arrangement of primary soil particles into aggregates. Using aggregate size, shape and distinctness as the basis for classes, types and grades, respectively, soil structure describes the manner in which soil particles are aggregated.

Aggregate Stability
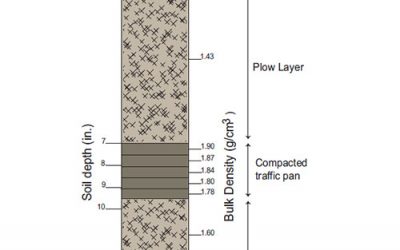
Bulk Density
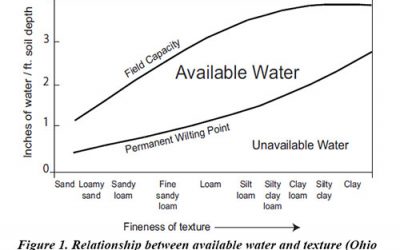
Water Capacity

Infiltration
Infiltration is the downward entry of water into the soil. The velocity at which water enters the soil is infiltration rate. Infiltration rate is typically expressed in inches per hour. Water from rainfall or irrigation must first enter the soil for it to be of value.
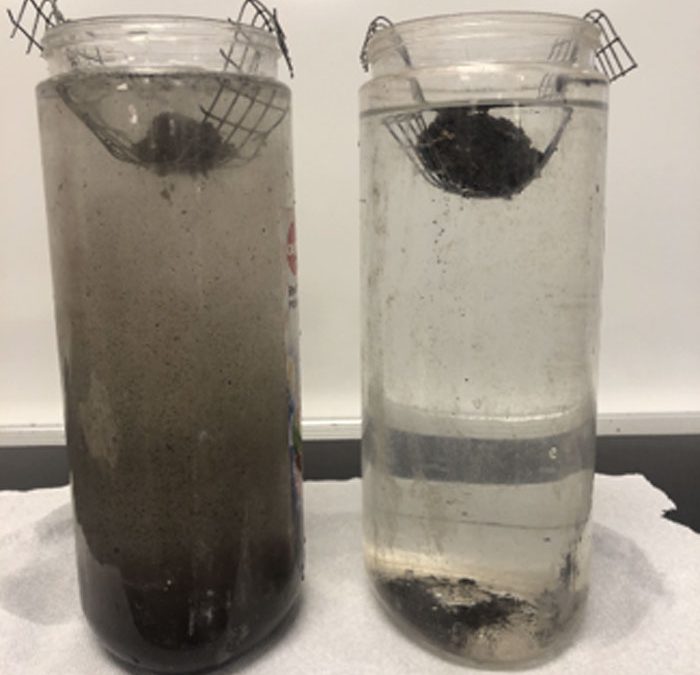

Slaking

West River Soil Health School Registration Open!
In 2024, the South Dakota Soil Health Coalition will host an additional Soil Health School in west of the Missouri River! The 2024 West River Soil Health School with be held June 26-27 near Caputa, SD! This school will focus on issues specific to the land, climate, and ag production systems of wester South Dakota. Class size is limited, so early registration is strongly encouraged!
News & Events
Farmer reaps higher yields by interseeding soybeans
By Stan Wise Alex Frasier has spent a lot of time studying what it takes to grow a successful crop. After studying ag production and precision technology at Lake Area Technical College, he has worked in ag retail and currently works as an agronomist in Aberdeen, SD....
Farm and ranch innovators to share new ideas at Soil Health Conference
By Stan Wise PIERRE, SD — Before Cooper Hibbard came home to manage his family’s ranch, he studied ag business, rangeland resources and Spanish at California Polytechnic State University and then worked on ranches all over the world. That education and experience...
Wintertime is decision time
By Stan Wise PIERRE, SD – It’s often said that the best time to start improving your land was 20 years ago, but the second-best time is right now. That statement might be harder for ranchers to swallow with winter on their doorstep, nothing growing in their pastures,...


